Only about 1 in 5,000 drugs ever makes it to market. Thus the prospect of developing new drugs represents a considerable risk. The introduction of cloud-based simulations promises to decrease that risk--and to spur rapid changes in the pharmaceutical industry.
Shorter Time to Market
The process for bringing a drug to market is not only expensive, but also incredibly lengthy; it often takes ten years or more. Drug trials have multiple phases, each of which is critical to ensure the drug’s safety and efficacy. However, this long trial period is detrimental when there is a public health emergency (for instance the 2015-2016 Zika outbreak). This has also been a serious drawback in less sensational scenarios, such as when an annual flu vaccine is a “mismatch” for the circulating strains of the virus.
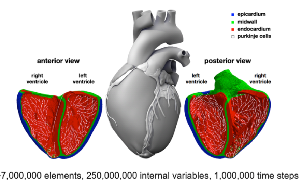 |
| The Living Heart Project used simulations to evaluate the risk of drug-induced arrhythmias. |
While simulations cannot completely replace conventional drug trials, they can considerably shorten the time required for trials, which is already well known in the pharmaceuticals industry. One promising application is the use of cloud-based simulations for evaluating a drug’s potential side effects. The Living Heart Project, for instance, used advanced electro-physiological modeling to study drug-induced arrhythmias of a human heart.
The conventional process for evaluating the risk for this potentially life-threatening side effect currently takes years and involves both animal and human studies. Because they used cloud-based HPC resources for their in silico simulations, Living Heart Project researchers could assess the risk much more quickly and safely.
Enablement of Wearable Technologies
Wearables have been used by consumers to collect their own individual health data for years, and experts have long known that these technologies held tremendous promise to revolutionize medicine. But gathering and using data collected from wearables has presented a significant challenge, simply because they have the potential to generate massive volumes of data. Consider that the average amount of data collected for the standard 400 drug trials is about 160 Terabytes--but a single trial using wearables might generate up to 80 Terabytes.
Storing and processing all that data requires vast computational power, making cloud-based simulations an ideal option. Pairing cloud simulations with data from wearables offers a key benefit: drug trials and other experiments can move to a more “remote patient-centered” model, that is, participants will not always have to be physically located where the drug trial is taking place.
This means that it will be much easier to get a larger, more representative sample of patients for medical studies. Furthermore, the use of wearable technologies also drastically decreases the amount of data that must be collected manually. Ultimately the ability to incorporate wearable technologies in medical trials, enabled by cloud simulation technology, can drastically decrease the time and cost associated with medical trials.
More Personalized Medicine
At the turn of the 21st century, the original conceptualization of personalized medicine is the use of an individual’s DNA to create an individualized drug treatment. That definition has evolved in the ensuing decades. Today drug companies are under intense pressure to develop a broad range of personalized medical interventions, from drugs to remote monitoring algorithms.
The development of these personalized interventions for individuals or small groups that share genetic makeup remains incredibly expensive--even as the industry also faces incredible pressure to lower costs for consumers. Cloud simulations have already proven an ideal means for making personalized medicine more profitable; they can assist in determining which treatments are most likely to work for individual patients, decreasing the risk of subjecting patients to treatment protocols that are ineffective, costly or invasive.
Democratization of the Industry
Some big names in pharmaceuticals, most notably GlaxoSmithKline and Pfizer, have already adopted various cloud technologies to accelerate or simplify the drug development process. But cloud simulations and other tools are also accessible to small and mid-size organizations because they can be much more cost-effective than on-premises solutions, which require the purchase and ongoing maintenance of both hardware and software.
This accessibility has already contributed to the democratization of the pharmaceuticals industry, enabling smaller companies to compete more readily with major pharmaceutical companies. The trend will undoubtedly continue, and it’s likely that significant drug breakthroughs will begin to come more often from relatively unknown companies.
Introduction of Less Invasive Alternative Treatments
Myriad medical conditions are managed with drugs because other treatments are too invasive risky. But cloud simulations can be used to make these treatments much safer for patients--potentially contributing to decreased demand for various categories of pharmaceutical products.
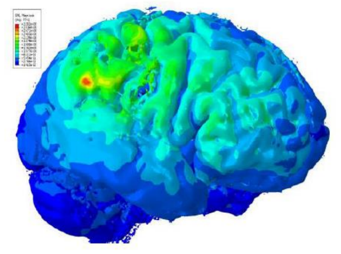 |
| Cloud-based simulations have enabled a non-invasive treatment for schizophrenia. |
A great example is the treatment of schizophrenia. Today, most patients control symptoms of this illness with powerful psychotropic drugs that must be taken regularly and can cause numerous unpleasant side effects.
However, these side effects might be preferable to the potential side effects of deep brain stimulation, a permanent but highly invasive treatment that requires the implantation of electrodes deep in a patient’s brain.
Using cloud-based simulations, scientists have developed a new therapy, transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS), which is a non-invasive neuro-stimulation that can be safely used to treat not only schizophrenia, but also depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, migraines, and chronic pain.
Hybrid Cloud as the First Step
The adoption of high-performance cloud technologies has been relatively slow in the pharmaceutical industry, largely due to concerns over security. After all, the development of new drugs requires the collection of highly sensitive data, including patient information and intellectual property.
One way to address data security issues is to use a hybrid model, which includes end-to-end security based on a virtual private network. Confidential information can be stored on-premises, while the public cloud can be used to as needed, for instance to increase computing power for complex simulations, which could use anonymized data that no longer include patient identifiers. A cloud provider familiar with HIPAA and other regulations concerning patient confidentiality can help ensure that any cloud-based solution is fully compliant.
Thanks to the introduction of cloud-based simulations, the pharmaceuticals industry is poised to shift rapidly. These changes will not only reduce costs for pharmaceuticals companies, but they will also result in safer, more effective care for patients.
Related Resources
 |
 |
 |
| Case Study: Implantable Planar Antenna Simulation with ANSYS HFSS in the Cloud | The Benefits of Cloud-Based Simulations for Personalized Medicine | Compendium of Life Sciences Case Studies, 2018 |




